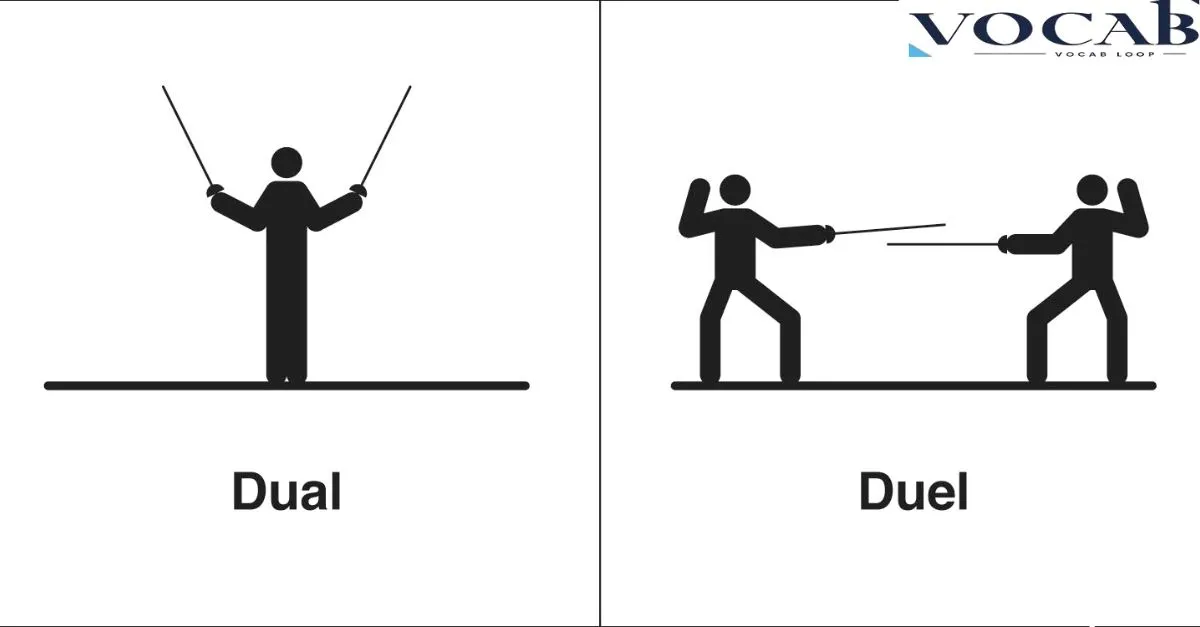
Duel and dual may sound similar, but their meanings are vastly different. Misusing these words can lead to confusion, especially when writing in professional or formal contexts. This article will clarify the distinction between duel vs dual by exploring their definitions, meanings, and appropriate usage.
By the end, you’ll understand the differences, learn helpful memory tricks, and be able to use each term accurately in your writing.
Understanding Duel and Dual
Is the Duel Word Correct?

Definition
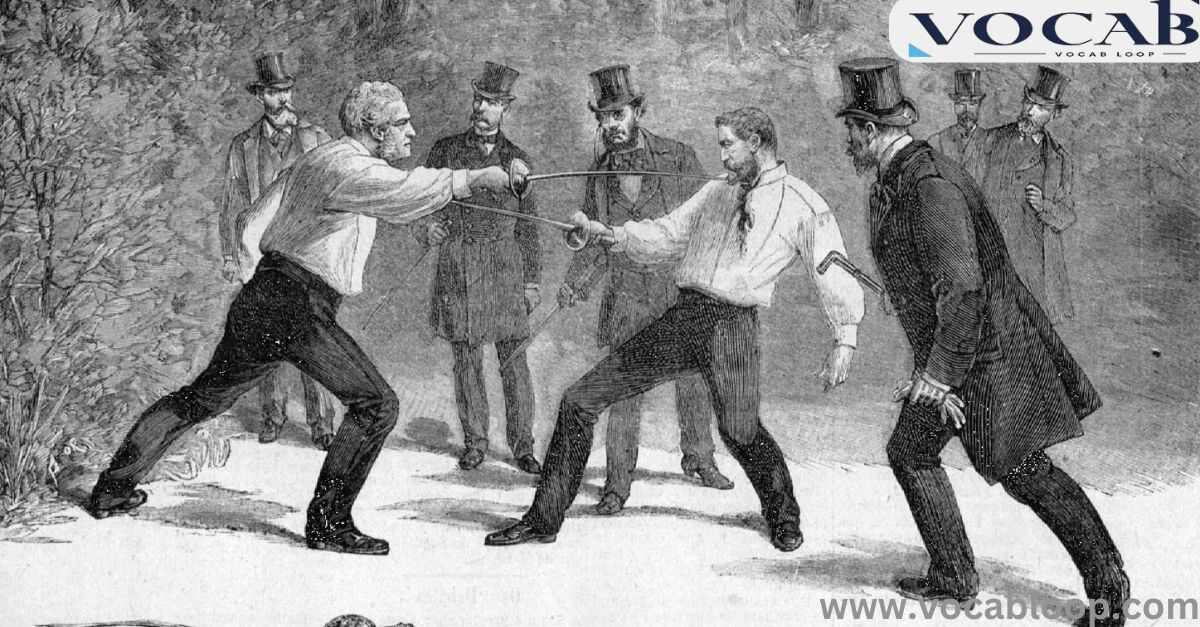
Duel is a noun and a verb that refers to a formal fight or contest between two people.
Often involving weapons, it is a traditional way to settle disputes, dating back to historical practices where honor challenges were a common means to resolve conflicts.
Meaning
The meaning of duel typically involves a sense of rivalry or confrontation. Whether in combat in literature or real-life historical duels, duel emphasizes conflict.
In the past, a duel was an organized battle or contest, sometimes resulting in serious injury or death. Today, it may also refer to intense verbal confrontations or rivalries in competitive settings.
Is the Dual Word Correct?
Definition
Dual is an adjective that means “two” or “double.” It refers to anything with a two-part explanation or dual purpose.
Dual is widely used in contexts where an item, role, or task has paired components or serves dual functions.
Meaning
The meaning of dual is closely tied to the concept of two-part or multi-use items. For example, a dual-core processor in technology describes a computer processor with two distinct cores, enhancing its performance.
Similarly, dual responsibility means having two main roles or functions. Dual does not imply rivalry or confrontation but rather unity in purpose or function.
Quick Summary
| Term | Definition | Usage Context |
| Duel | Formal fight or rivalry | Historical duels, conflicts |
| Dual | Something with two parts or uses | Dual-core processor, roles |
Duel and Dual Parts of Speech
Duel acts as both a noun and a verb. As a noun, it refers to a formal fight, and as a verb, it means to engage in one.
Dual functions solely as an adjective, describing anything with two aspects or paired elements. This distinction makes each term’s usage unique and critical for precise writing.
Pronunciation of Dual and Duel
Though duel and dual look alike, they are pronounced slightly differently. Duel sounds like “jewel” (/ˈdjuː.əl/), while dual is pronounced to emphasize the concept of “two” (/ˈdjuː.əl/).
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Aspect | Duel | Dual |
| Definition | Formal fight or rivalry | Two-part or dual-purpose |
| Usage | Combat scenes, rivalries | Paired items, multi-use functions |
| Parts of Speech | Noun, Verb | Adjective |
| Key Contexts | Fight examples, historical settings | Dual roles, tech contexts |
Which One is More Acceptable?
Both words are correct but must be used in the right contextual meaning. When describing combat or a challenge, duel is the suitable word.
If referring to paired roles or dual functionality, then dual is the better choice. Misusing either word can lead to ambiguity, especially in professional or technical writing.
Trick to Remember the Difference

An easy trick to remember is to associate duel with “fight” and dual with “double.” Duel is about confrontation or rivalry, while dual describes things with two parts or purposes.
Origins of Duel vs Dual
Duel
The word duel comes from the Latin “duellum,” meaning war. This connection to conflict and rivalry highlights its historical use as a term for combat definition in resolving personal disputes, often involving a weapon combat or challenge for honor.
Dual
Dual originates from the Latin “dualis,” which means “two.” The term evolved to describe anything with two elements, such as dual responsibilities or dual-core processors. “People frequently use it today in both daily language and technical contexts, emphasizing the idea of paired components.”
Synonyms of Duel vs Dual
Duel
- Fight
- Contest
- Confrontation
- Challenge
- Combat distinction
Dual
- Double
- Paired
- Binary
- Twofold
- Multi-use
Everyday Usage Examples

Duel
- The warriors prepared for their final duel.
- He issued a duel challenge to settle their dispute.
- The duel was held at sunrise with swords.
- They fought a duel to defend their honor.
- The movie featured a classic duel scene.
- She witnessed a duel in the historical play.
- Their duel was intense and life-changing.
- Famous historical duels were often fatal.
- The rivalry led them to a duel.
- In medieval times, a duel settled serious matters.
Dual
- She holds dual citizenship.
- The computer has a dual-core processor.
- His job has dual responsibilities.
- They used dual cameras for better coverage.
- The product offers dual functionality.
- She manages dual roles in the company.
- Dual goals guide their strategy.
- His vehicle has dual climate control.
- The service provides dual benefits.
- He is skilled in dual tasks.
FAQs
What’s the main difference between duel and dual?
“Duel” refers to a fight or rivalry, while “dual” describes a two-part function or purpose.
Can “duel” be used as an adjective?
No, duel is a noun or verb. Dual serves as an adjective.
Are there idioms or phrases with “dual” or “duel”?
Yes, examples include “duel of wits” and “dual nature.”
Why do people confuse these two words?
They sound similar, but have very different meanings.
Can “duel” and “dual” be used interchangeably?
No, they have specific meanings and cannot be swapped.
Conclusion
The words duel and dual may appear similar but serve entirely different purposes in language. Duel reflects conflict and rivalry, common in historical and literary contexts, while dual describes anything with two elements or paired roles, often seen in modern technology and descriptions of combined tasks.
By understanding their meanings and usage, you can communicate more effectively and avoid common language mix-ups.

Alex Hormozi is a seasoned blogger at Vocab Loop, known for his deep insights into language, vocabulary, and grammar. With years of experience in writing, Alex shares practical tips and effective strategies to help readers improve their linguistic skills and enhance their writing abilities.